Yoga vs physical activity: A comparative study of stress and sleep in young adults
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23921/amp.2025v8i1.00075Keywords:
Medical students, Mental health, Physical activity, Sleep quality, Stress, Yogic breathingAbstract
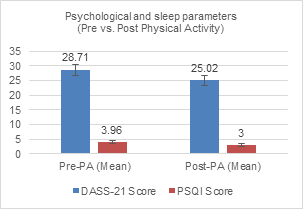
The high prevalence of stress and sleep disorders among medical students necessitates effective, non-pharmacological interventions. While both yogic breathing and physical activity are beneficial, their comparative efficacy on these specific outcomes remains unclear. This study aimed to compare the effects of a structured yogic breathing intervention and moderate-intensity physical activity on perceived stress levels and subjective sleep quality in healthy medical students. A prospective, randomized controlled trial was conducted with 170 participants allocated to either a Yogic Breathing Group (n=85) or a Physical Activity Group (n=85). The intervention lasted five weeks, with sessions conducted five days per week. The primary outcomes, psychological stress and sleep quality, were assessed using the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21) and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), respectively, at baseline and post-intervention. Data were analyzed using paired t-tests and Analysis of co-variance. Both groups showed significant within-group improvements in stress (p<0.001). However, between-group analysis revealed that the Yogic Breathing group achieved a significantly greater reduction in DASS-21 scores compared to the Physical Activity group (mean ?: -14.43 ± 6.21 vs. -3.69 ± 5.12; p<0.001). Conversely, the Physical Activity group demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in PSQI scores than the Yogic Breathing group (mean ?: -0.96 ± 1.42 vs. -0.40 ± 1.05; p=0.012). Yogic breathing was superior for reducing perceived stress, whereas physical activity was more effective for enhancing sleep quality. The results indicate that both approaches complement each other rather than replace one another. Selecting the right approach should depend on the specific needs, helping to provide a more individualized plan for well-being.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Sheikh S, Rostami A, Shahbazi A, Abdollahi Nezhad F, Khazai O, Arbabisarjou A. Clinical effectiveness of guided breathing exercises in reducing anxiety, stress, and depression in COVID-19 patients. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):26620.
Biggs A, Brough P. Stress and Coping Theory. In: Liamputtong P (eds). Handbook of Concepts in Health, Health Behavior and Environmental Health. Singapore: Springer; 2025:1-23.
McEwen BS. Neurobiological and systemic effects of chronic stress. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2017;1:2470547017692328.
Schakel L, Veldhuijzen DS, Crompvoets PI, Bosch JA, Cohen S, van Middendorp H, Joosten SA, Ottenhoff THM, Visser LG, Evers AWM. Effectiveness of stress-reducing interventions on the response to challenges to the immune system: A meta-analytic review. Psychother Psychosom. 2019;88(5):274-286.
Arnsten AF. Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(6):410-422.
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK, Sanacora G, Krystal JH. Synaptic plasticity and depression: new insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat Med. 2016;22(3):238-249.
Kavitha N, Pal P, Pal GK, Bharadwaj B, Nanda N. Effects of slow breathing exercises on cardiac autonomic functions in anxiety disorder-A randomised control trial. Ann Neurosci. 2024:09727531241266094.
Kuppusamy M, Kamaldeen D, Pitani R, Amaldas J, Ramasamy P, Shanmugam P, Vijayakumar V. Effects of yoga breathing practice on heart rate variability in healthy adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. Integr Med Res. 2020;9(1):28-32.
Lin LL, Chen YJ, Lin TY, Weng TC. Effects of resistance training intensity on heart rate variability at rest and in response to orthostasis in middle-aged and older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(17):10579.
Bellón JÁ, Conejo-Cerón S, Sánchez-Calderón A, Rodríguez-Martín B, Bellón D, Rodríguez-Sánchez E, Mendive JM, Ara I, Moreno-Peral P. Effectiveness of exercise-based interventions in reducing depressive symptoms in people without clinical depression: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. 2021;219(5):578-587.
Lovibond SH, Lovibond PF. Manual for the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales. 2nd ed. Sydney: Psychology Foundation of Australia; 1995.
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989;28(2):193-213.
World Health Organization. Global recommendations on physical activity for health. Geneva: WHO; 2010. ISBN: 9789241599979. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241599979
American Heart Association. American Heart Association recommendations for physical activity in adults. Dallas (TX): American Heart Association (AHA); 2024. Available from: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/aha-recs-for-physical-activity-in-adults
Staniszewski M, Tkaczyk J, K?ska A, Zybko P, Mróz A. Effect of rest duration between sets on fatigue and recovery after short intense plyometric exercise. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):15080.
Streeter CC, Gerbarg PL, Saper RB, Ciraulo DA, Brown RP. Effects of yoga on the autonomic nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric-acid, and allostasis in epilepsy, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Med Hypotheses. 2012;78(5):571-579.
Sharma M. Yoga as an alternative and complementary approach for stress management: a systematic review. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2014;19(1):59-67.
Rebar AL, Stanton R, Geard D, Short C, Duncan MJ, Vandelanotte C. A meta-meta-analysis of the effect of physical activity on depression and anxiety in non-clinical adult populations. Health Psychol Rev. 2015;9(3):366-378.
Hariprasad VR, Sivakumar PT, Koparde V, Varambally S, Thirthalli J, Varghese M, Basavaraddi IV, Gangadhar BN. Effects of yoga intervention on sleep and quality-of-life in elderly: A randomized controlled trial. Indian J Psychiatry. 2013;55(Suppl 3):S364-S368.
Nagendra RP, Maruthai N, Kutty BM. Meditation and its regulatory role on sleep. Front Neurol. 2012;3:54.
Kredlow MA, Capozzoli MC, Hearon BA, Calkins AW, Otto MW. The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. J Behav Med. 2015;38(3):427-449.
Lo JC, Ong JL, Leong RL, Gooley JJ, Chee MW. Cognitive performance, sleepiness, and mood in partially sleep deprived adolescents: The need for sleep study. Sleep. 2016;39(3):687-698.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Quench Academy of Medical Education and Research (QAMER)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors warrants and represents that the submitted MANUSCRIPT is an original work and has not been published before in any form, and that it does not infringe upon any copyright or other right(s), that it does not contain infringing, libelous, obscene or other unlawful matter, that he/she is the sole and exclusive owner of the rights here-in conveyed to the Publisher, and that he/she has obtained the customary permission from the copyright owner or his legal representative whenever a text/passage from copyrighted material is quoted or a table or illustration from such material is used. The Author(s) will indemnify the Publisher for, and hold the Publisher harmless from any loss, expense or damage occasioned by any claim or suit by a third party for copyright infringement or arising out of any breach of the foregoing warranties as a result of publication of the Article. The Article shall be delivered to the Publisher free of copyright charges. In the event that the Article is not accepted and published by Publisher, this agreement becomes null and void.
Sherpa/Romeo publisher policy can be viewed at Annals of Medical Physiology - Sherpa/Romeo Policy
Plum X metrics
Article level metrics are shown here









