Electrocardiographic changes in patients with pre-eclampsia
ECG changes in pre-eclampsia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23921/amp.2019v3i1.26774Keywords:
ECG, Pre-eclampsia, QRS, QTc, Sokolow-Lyon indexAbstract
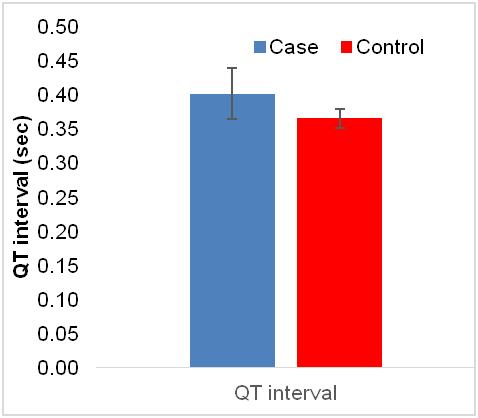
Pre-eclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy that is associated with elevated maternal risk for cardiovascular disease. Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes in pre-eclampsia have been documented in some studies. Electrocardiography has recently emerged as a useful tool to evaluate cardiovascular complication during and after pregnancy. The present study was therefore undertaken to find out electrocardiographic changes in pre-eclamptic women, visiting Regional Institute of Medical Sciences, Manipur. The aim of this study was to determine the electrocardiographic changes in both pre-eclampsia and age matched normotensive pregnant women. In this study, 25 pregnant women (gestational age >20 weeks) with pre-eclampsia in the range of 18 to 45 years of age were recruited and compared with the equal number of age matched normotensive pregnant women. ECG parameters of pre-eclamptic women were compared with those of normotensive pregnant women. The data were then analyzed using SPSS software. Pre-eclamptic women showed significantly longer QRS (0.10±0.02 sec vs 0.09±0.05 sec), prolonged QT (0.401±0.03 sec vs 0.365±0.003sec) and QTc (457.73±37 msec vs 416.47± 25.4 msec) than control group. The study shows that electrocardiography can be used to evaluate cardiovascular risk in pre-eclamptic women.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Duley L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 2009 Jun; 33(3):130-7.
Konar H. DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics. 7thed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers; 2013.
Sogani S, Varma V, Sarkar PD. Estimation of thyroid hormones levels in preeclamptic pregnant women: an early predictor of the disease. Al Ameen J Med Sci. 2015; 8(4):266-70.
Baumert M, Seeck A, Faber R, Nalivaiko E, Voss A. Longitudinal changes in QT interval variability and rate adaptation in pregnancies with normal and abnormal uterine perfusion. Hypertens Res. 2010 Jun; 33(6):555-60.
Angeli F, Angeli E, Verdecchia P. Novel electrographic patterns for the prediction of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy – from pathophysiology to practical implications. Int J Mol Sci 2015 Aug 7; 16(8):18454-73.
Murphy MS, Seaborn GE, Redfearn DP, Smith GN. Reduced heart variability and altered cardiac conduction after preeclampsia. PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25; 10(9):e0138664.
Raffaelli R, Prioli MA, Parissone F, Prati D, Carli M, Bergamini C, Cacici G, Balestreri D, Vassanelli C, Franchi M. Pre-eclampsia: evidence of altered ventricular repolarization by standard ECG parameters and QT dispersion. Hypertens Res. 2014 Nov; 37(11):984-8.
Isezuo SA, Ekele BA. Eclampsia and the abnormal QTc. West Afr J Med. 2004 Apr-Jun; 23(2):123-7.
Zangeneh M, Veisi F, Malekkhosravi S, Rezavand N, Nankali A, Rezaei M, Ghadami MR, Karami A. Electrocardiographic changes in healthy and pre-eclamptic pregnant women. J Kermanshah Univ Med Sci. 2012; 16(4):e78789. [Article in Persian]
Melchiorre K, Sharma R, Thilaganathan B. Cardiovascular implications in preeclampsia: an overview. Circulation. 2014 Aug 19; 130(8):703-14.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Quench Academy of Medical Education and Research (QAMER)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors warrants and represents that the submitted MANUSCRIPT is an original work and has not been published before in any form, and that it does not infringe upon any copyright or other right(s), that it does not contain infringing, libelous, obscene or other unlawful matter, that he/she is the sole and exclusive owner of the rights here-in conveyed to the Publisher, and that he/she has obtained the customary permission from the copyright owner or his legal representative whenever a text/passage from copyrighted material is quoted or a table or illustration from such material is used. The Author(s) will indemnify the Publisher for, and hold the Publisher harmless from any loss, expense or damage occasioned by any claim or suit by a third party for copyright infringement or arising out of any breach of the foregoing warranties as a result of publication of the Article. The Article shall be delivered to the Publisher free of copyright charges. In the event that the Article is not accepted and published by Publisher, this agreement becomes null and void.
Sherpa/Romeo publisher policy can be viewed at Annals of Medical Physiology - Sherpa/Romeo Policy
Plum X metrics
Article level metrics are shown here









